Processing¶
A competition requires an evaluation, an evaluation. This consists of three Javascript functions that describe the life cycle of the competition. In order to To understand how it works, it is useful to first understand the basic way it works understand.
Basics¶
During a competition, each participant’s devices deliver an endless stream of Device events that are sent to the sports server. A participant is therefore from the point of view of of the system is nothing more than a data record with name, avatar, … and above all: a endless stream of waypoints.
The time measurement alone determines which of these waypoints are relevant and which are not can be ignored. There are several timestamps that are important:
- The entire competition has a start and end timestamp. Only events that take place in are relevant at all.
- Each participant is subjected to several time measurements. Only events that are also relevant if they take place during an active measurement of the participant.
A ranking data record is saved for each participant in each competition. This Data record is updated for every incoming event that takes place during a time measurement calculated. Which data is stored in this data set is completely up to the Developer of the reducer. At the beginning of the competition (or at the first Time measurement), an initial data record is created and a new data record is created for each incoming device event this data record is changed.
The sports server evaluates these data records at regular intervals to produce a ranking and display this ranking.
A competition looks like this:
- Initialisation of one data record per participant
- For each incoming device event, this data set is mutated by adding a user-defined function is called, to which the current data set and the current event as a parameter.
- A new ranking is calculated and published at regular intervals
Code¶
In the following, a sample code will be developed which can serve as a basis for to develop its own reducers. The system to be developed should represent a ranking, which selects the participant with the highest speed as the winner.
Initialisation¶
The initialisation function must have the name initValue and a data structure
which serves as the initial value for a participant.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
The code returns an object that provides the maxspeed field and is linked to the
Value 0 is initialised, i.e. for each participant a data record of the form
1 2 3 | |
Reducer¶
If the subscriber’s device now supplies a signal, the function reduce
is called. This function receives the current data set data as a parameter and the
Device signal event as parameter.
While the structure of the data Parameter should be known to the developer (the
Initial value is generated with the initValue), an event has the following structure:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | |
To recognise the participant with the highest speed as the winner in the ranking
the reduce Function must remember the highest speed:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
The system only checks here whether the speed contained in the device data record
is greater than that stored in the participant data record. If this is the case, this
Speed is saved as the new maximum speed. The jslog function can be
can be used to generate log outputs, which are displayed in the Sports app.
can be tracked.
Each data record sent by the device is mapped to the reduce function Function to
one subscriber data set reduced, i.e. the incoming stream of events is reduced to a single data set
Data set is compressed. In this simple example, it is simply the maximum
Speed, but of course there are endless possibilities here.
Ranking¶
Ultimately, however, a ranking list is required, which is also sorted by the sports app
has to be sorted. To ensure that this sorting and display is independent of the user-defined
Data structure, a third function must be made available, the
rankValue.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
This function returns a triple with three integers. The sorting of the Participants is then determined in such a way that the participant with the highest score at index 0 of the Is the winner. If there are several participants with the same value, the index 1 and if this is also the same, index 2 is used. If all three values are equal, the participants are considered to be equal in points.
In the example above, the stored speed is multiplied by 100, as it is
is a decimal number that indicates the speed in km/h. This value is
is then converted to an integer (using the standard JS function parseInt). The two
other values are returned as 0 and can be omitted in this case
i.e. it would also be sufficient to simply create an array with a single element
to be returned.
Debugger¶
For the development of reducer and ranking Functionalities, the system offers a
integrated debug mechanism. For this purpose, the functions can be debugged with
Events can be played through. Each event can be played as a single step or automatically
can be fired.
Generator¶
The basis for the debugger is a generator. This is an entity which can generate a current of events. There are three different generator types for this:
-
String-based
A JSON array is entered in an edit area, which corresponds to the event format of the Platform. The syntax can be checked, but whether the the desired events are only generated at runtime. -
Database-based
Events can also be selected directly from the database. To do this, two Timestamp (start, end) and the source (Comeptition,Team,Participant) selected. The system retrieves the corresponding events and saves them sorted redundantly in chronological order. Caution: For large time periods this means that it takes longer for all data to be buffered. In addition takes up a lot of space in the database, i.e. large DB generators should only be used for replays and then deleted again. -
GPX based
Various GPX data can be uploaded here from the tracking data extracted are stored. An IMEI as well as a time stamp and an interval are added to each piece of data is required. The system then uses the positions, the IMEI and the time information to generate a List of events. If desired, this list can then be converted into a string-based Generator, so that individual attributes of the events can still be converted there can be adjusted manually.
If a suitable generator has been created, it can be used to debug an Evaluation
be utilised.
Debugger data¶
The debugger expects three fields that can/must be filled:
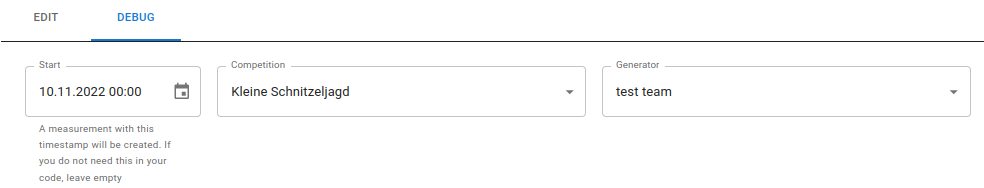
- Start timestamp
So-calledreducercan be accessed in anmeasurements. These are Time measurements that are created when the measurement is started. If thereducerrequires a Measurement, a time measurement can be created by specifying the time stamp, which can then be queried in the code. If the code does not require this, the field be left blank. - Competition
All currently available competitions are displayed in the list. The debugger this is required to create a suitable ranking for all participants, which is then used by thereduceris filled with data. - Generator
The generator supplies a current of events.
Initialisation¶
The debug session is started by clicking on Reset
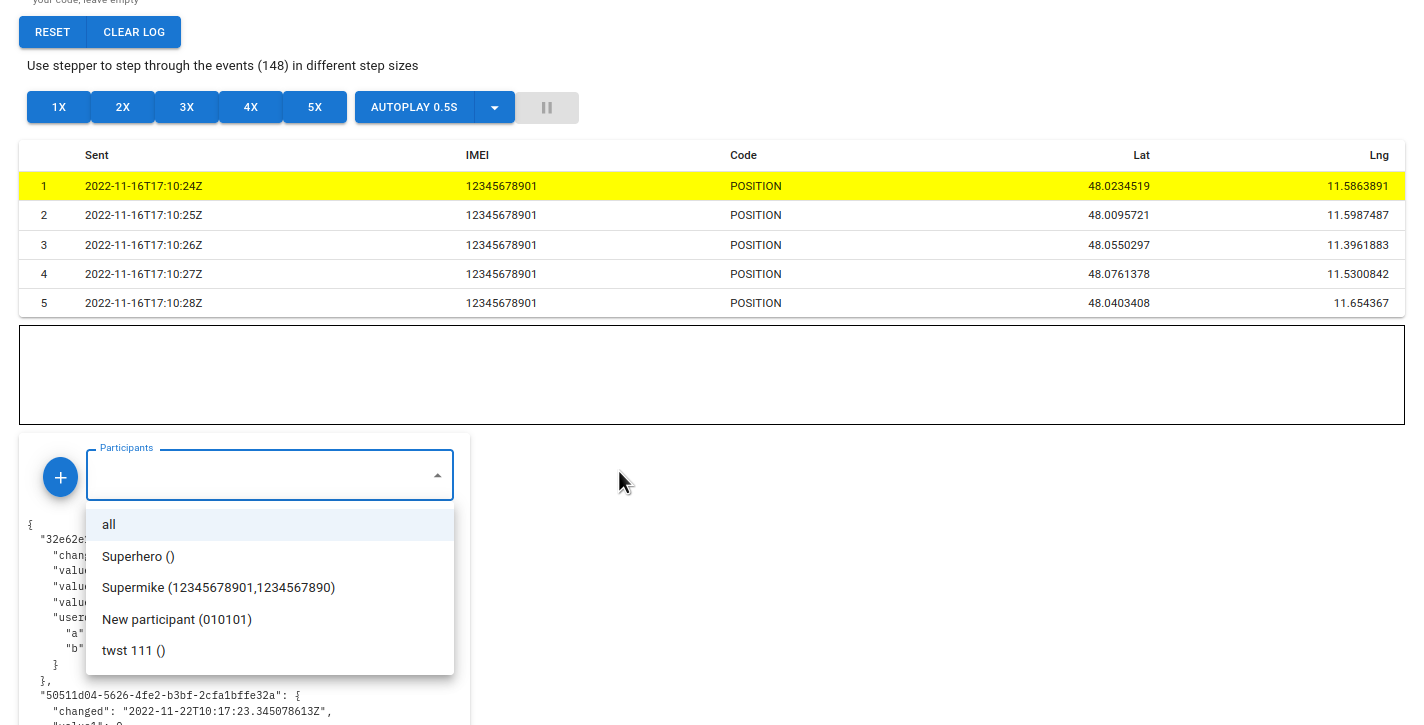
The system loads the events from the generator and displays a section of them. The yellow is always the data record that will be executed next.
With the buttons 1x, 2x… one, two, … Events can be executed against the reducer
become.
Directly below the list of events is an output area for the logs of the reducer and
below this are the runtime data of the Competition. By selecting a participant in
in the drop-down list can be used to restrict the display of data to this participant. With
the PLUS Button can be used to create several such display areas, each of which can be
indicates a specific subscriber.
Once a debug session has run through (all events), it can be restarted using Reset
can be started.
Step-by-step debugging¶
After a debug step, the list of events shows the new (future) record in yellow, the output shows any logs that may have been made and the data area shows the dataset of the selected participants:
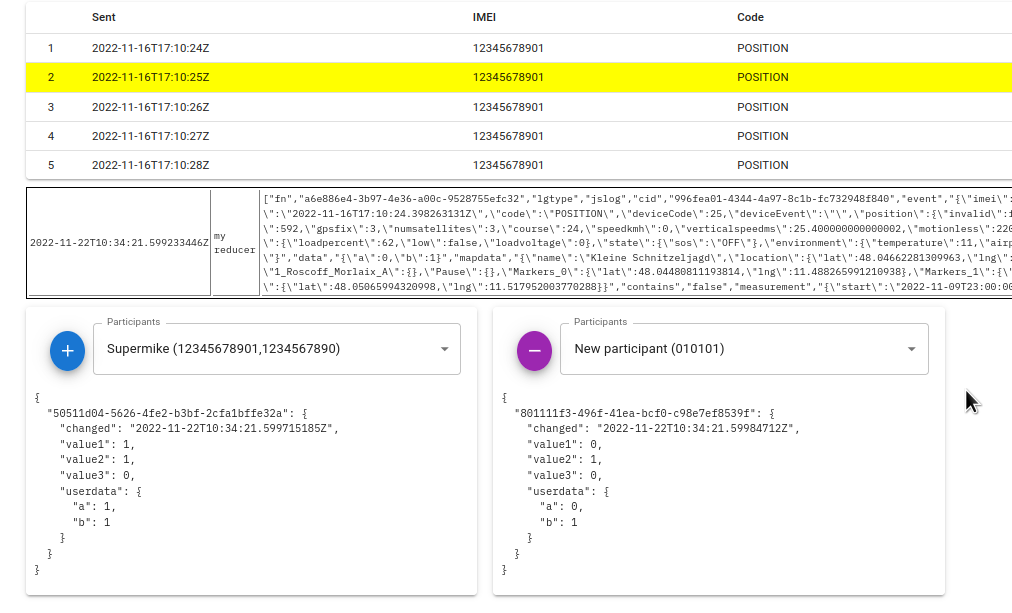
The data area always consists of a structure with the following values:
-
value1…value3
These values are the results of the rank function -
userdata
The user data area contains the data that the Reducer collects after each step is returned.
Autoplay¶
With the help of automatic debugging, the events from the generator can be analysed in chronological order
Sequence. Attention: The events all contain a Sent Timestamp,
i.e. the speed at which the events are processed should reflect the logic of the
Reducers.
When the debugger is running in automatic mode, you can press the pause button at any time and then be rejected in single-step mode.
Provided objects¶
As can be seen in the example, the reducer Function always receives the current data set and
the current event is transferred. In addition to this data, the function also contains other
Data available.
Logging¶
There is a function jslog with which log outputs can be carried out. The
Signature of the function is:
1 | |
The first parameter is therefore a log message, followed by key/value pairs, where the key must be a string and the value is freely definable. In the example above the following call:
1 | |
Here new maxspeed found is the log message; this is followed by the key/value pairs ("event",
event) und ("data",data).
Map data¶
Basic data on the displayed map is contained in the variable mapdata.
mapdata.name
The name of the competitionmapdata.baselayer
The name of the layer setmapdata.opacity
The value of the set opacitymapdata.zoomlevel
The value of the set zoom levelmapdata.location
The position of the competition marker
In addition, mapdata also contains the saved courses and regions with the
Names specified in the system. A course is a collection of lines and the
Course has a function intersects, e.g.
mapdata.Finish.intersects(pos1, pos2)
If there is a course with the nameFinish, this function can be used to query whether this course can be matched with a connecting line from the two transferred Positions (events can also be transferred directly; the system extracts position there independently).mapdata.course.polyline.nearestEdge(pos, {index:0, reset:true, lap:0})
If there is a course with the namecourseand in this course there is a polyline calledpolyline, then this function can be used to search for the next corner of the polyline that is closest to the position. The transferred index is used to only subsequent corners can be found. The parameterresetspecifies whether at the end of the course is searched again from the beginning; in this case a lapcounter is returned.
The function returns an object with the attributesindex,resetandlapwhich can be passed to the subsequent call. The return contains furthermore, the fieldsgap(distance to the found point) anddistance(distance travelled Total distance (including lap count if applicable). The LatLng position found is is set in theroutelocationfield.
In a region, there is a function contains which only has a single position (or
an event) is transferred. If this position is contained in the region, it returns
Function has the value true.
Measurement¶
A participant can have several time measurements. To request these, use the
measurement Object. This provides a function getAt, which can be used to
Time measurement for the specified device event.
1 2 | |
This code asks the system for the start of the time measurement for the current
Device event. The start attribute is a JavaScript data object with the timestamp.
This can be used, for example, if a race has a fixed mass start
and a clear signal.
Race¶
The timestamps of the start and end of the event are saved in race:
race.start
The start of the event (can also benull)race.end
The end of the event (can also benull)
Info
These two timestamps are not the start and end time of the competition. These are saved in the Measurements and can be saved for each participant be different. If there are several time measurements, there may also be there will be different start times for each participant.
Via the race Object it is possible to stop the time measurement; the function
stop(evt) which requires an event as a parameter. If this function is called
the time measurement for the device contained in the event is ended and the sent Timestamp as
End of time measurement used. Ex:
1 2 3 4 | |